What is Data Loss Prevention(DLP) | How does it works?
What is Data Loss Prevention(DLP) | How does it works?
Data loss prevention (DLP) is a strategy for ensuring that end users do not send critical or sensitive information outside the corporate network. DLP is also used to describe software products that help a network administrator control what data end users can transfer. These solutions execute responses based on policy and rules defined to address the risk of inadvertent or accidental leaks, or exposure of sensitive data outside authorized channels.

Data loss prevention solutions are growing in popularity as enterprises look for ways to reduce the risk of sensitive data leaking outside the company. Gartner estimates that by 2021, 90% of organizations will have implemented at least one form of integrated DLP, up from 50% in 2017. A DLP solution relies on several core technologies that enable its engine to accurately identify the sensitive data that enterprise need to secure and take remediation action to prevent incidents.
DLP technologies are broadly divided into two categories –
Enterprise DLP: They are comprehensive and packaged in agent software for desktops and servers, physical and virtual appliances for monitoring networks and email traffic, or soft appliances for data discovery
Integrated DLP: It is limited to secure web gateways (SWGs), secure email gateways (SEGs), email encryption products, enterprise content management (ECM) platforms, data classification tools, data discovery tools and cloud access security brokers (CASBs).
What Type of DLP Solution is Right for Your Organization?
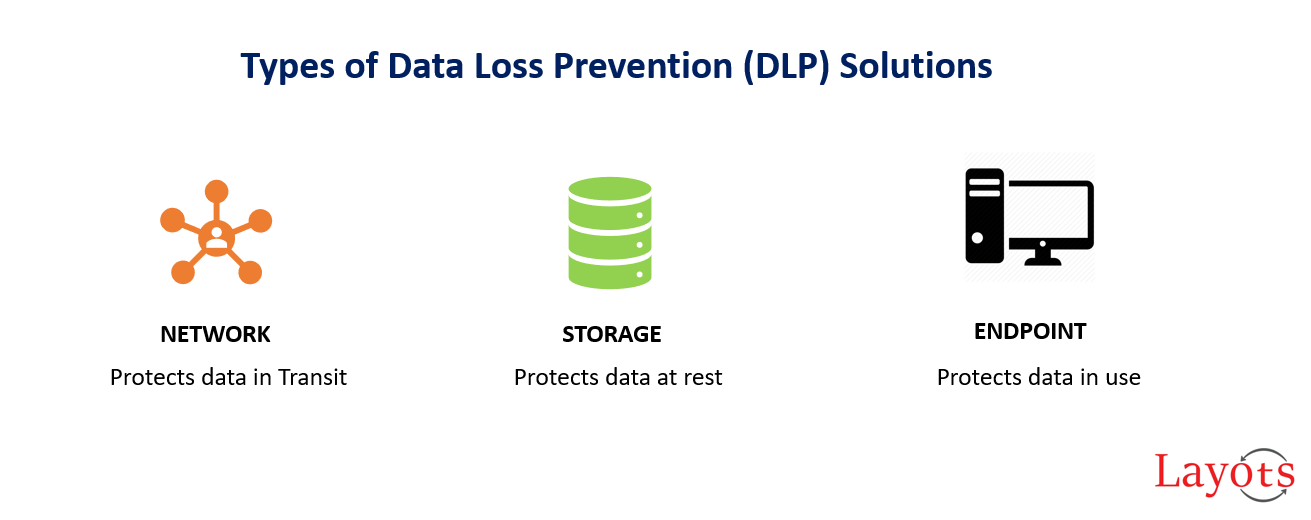
NETWORK DLP
- Protects an organization’s network processes, such as web application, email and FTP.
- Lives in the company’s network, and monitors data as it moves throughout the network.
- Maintains a database which provides details as to which data is being used and who is using the data.
- Provides visibility into all data in transit on their network.
STORAGE DLP
- Provides information about files stored and shared by users of an organization’s network.
- Enables viewing sensitive files shared and stored on the network.
- Provides visibility into information stored via on-premise storage equipment and cloud-based storage.
ENDPOINT DLP
- Monitors workstations, servers, and mobile devices such as laptops, mobile phones, external hard-drives and USB disks.
- Installed as an agent on endpoint equipment and prevents data leakage from the endpoints.
- Provides visibility into data stored on endpoints physically located inside and outside the organization.
Top reasons why your organization needs Data Loss Prevention?

- Data protection is one of the primary concerns when adopting cloud services. You can use DLP solutions to classify and prioritize data security. You can also use these solutions to ensure access policies meet regulatory compliance, including HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS.
- DLP tools can help you identify deviations from policy making it easier to correct misconfigurations.
- DLP tools can compare current configurations to compliance standards and provide proof of measures taken.
- DLP tools can provide visibility across systems, helping you ensure that data is secure no matter where it’s stored.
- Modern storage can be accessed from remote locations and through cloud services; laptops and mobile phones contain sensitive information and these endpoints are often vulnerable. It is becoming increasingly difficult to ensure that data is secure, making a data loss prevention strategy so important.
- DLP software products use business rules to classify and protect confidential and critical information so that unauthorized end users cannot accidentally or maliciously share data whose disclosure could put the organization at risk.
- In addition to being able to monitor and control endpoint activities, some DLP tools can also be used to filter data streams on the corporate network and protect data in motion.
- Business organizations go through major financial losses and reputational damage when they experience loss of sensitive data and other forms of enterprise information. Companies are now very much aware of these dangers and hence data protection has become the most vital thing to be deployed across the organisation.
Content analysis techniques

The idea behind content awareness is that although we want to use the context to gain more intelligence on the content, we don’t want to be restricted to a single context.
Rule-Based/Regular Expressions: The most common analysis technique employed in DLP involves an engine’s analyzing content for particular rules such as 9-digit US social security numbers, 16-digit credit card numbers, etc. This technique is considered to be an exceptional first-pass filter since the rules can be configured and processed swiftly, even though they can be prone to high false positive rates without checksum validation to detect valid patterns.
Conceptual/Lexicon: Using a combination of rules, dictionaries, etc., these policies are capable of alerting on completely unstructured ideas that challenge simple categorization. It will have to be customized for the DLP solution provided.
Statistical Analysis: Employs machine learning or other statistical methods such as Bayesian analysis to activate policy violations in secure content.
Pre-built categories: Pre-built categories with dictionaries and rules for common types of sensitive data, such as HIPAA, credit card numbers/PCI protection, etc.
Database Fingerprinting: This technique is also known as Exact Data Matching. It looks at exact matches from a database dump or live database. This is an option for structured data from databases even though database dumps or live database connections affect performance.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Your DLP Solution

Like any complex, mission critical system, it’s essential to evaluate your DLP solution and measure how much value you are deriving from it, and whether that value is gradually improving over time or declining. Here are six simple metrics that can help you catch issues with your DLP implementation or the underlying DLP policies.
1. Percentage of policy exceptions: Exceptions can be explained as one-off permissions given to individuals or groups via the DLP tool, with regard to data access or transfer. Exceptions indicates organizations data that is used outside the DLP policy and may be vulnerable. Monitor the number of exceptions, as a percentage of all data-related events, to see the extent to which the DLP policy is enforced.
2. Percentage of false positives: DLP systems generate a large number of alerts, and many of those turn out not to be real security incidents, which places a burden on security teams. The percentage of false positives of all alerts measures the effectiveness of your DLP tool at filtering out irrelevant alerts and identifying real data issues.
3. Alert response time: Measures the mean time taken to respond to DLP alerts (excluding false positives). In many cases, due to the large volume of alerts, security teams might respond to critical DLP alerts late, or even ignore some alerts altogether. Measuring alert response time can help you identify problems in the DLP implementation or process, which are preventing security staff from responding to critical data alerts.
4. Number, type and storage size of unmanaged devices: You must keep track of the amount of unmanaged devices that contain sensitive information. Such devices might include endpoints, servers, removable storage and cloud storage (depending on what is managed by your DLP system). All of these can act as departure points for sensitive information. Your DLP implementation should keep the number of unmanaged devices to a minimum, and if the number increases, consider switching to a solution which can manage more devices.
5. Percentage of databases which are fingerprinted: DLP solutions create a digital fingerprint of a relational database, which allows for tamper detection, traitor tracing (identifying the source of a leak), and validates the integrity of the data. Measure the percentage of databases which are fingerprinted at any given time to ensure you have solid control of sensitive data sources.
6. Data classification success rate: The initial action in any Data Loss Prevention solution is data classification. Data classification helps you identify and isolate sensitive information, and understand its context. DLP solutions have various techniques for automatically or semi-automatically classifying data. Measure the percentage of erroneous classifications to see how much sensitive data your DLP may be leaving behind.
The number of attempted and successful breaches at organizations of all sizes is rapidly growing. Sensitive data is an attractive target for attackers. It follows that employing the right DLP solution in the cloud encompassing accuracy, real-time monitoring, analysis of data in motion, incident remediation and data loss policy authoring is essential for successful cloud adoption.
If you’re interested in leveling up your IT security, you should start with our security experts from Layots to design your data security plan, and add functionality around it to fill in any gaps, like an Endpoint DLP solution.

Layots has 20+ years of unmatched experience in providing IT solutions. Our solutions offer speed, agility, and efficiency to tackle business challenges in the areas of data security, cyber security, service management, application development, automation, test & development environments and operations.

